Understand the statistics
Statistics enable you to improve items that will be used again in tests, determine the validity of a test's score in measuring student aptitude, and identify specific areas of instruction that need greater focus.
Item statistics
Item statistics assess the items that make up a test.
Item difficulty (P)
P Value refers to the degree of challenge for items based on the percentage of students who chose the correct answer. Item difficulty is relevant for determining whether students have learned the concept being tested.
Also Called: P Value, Difficulty Index
Score Range: 0.00 to 1.00
The higher the value, the easier the question. In other words, if no one answers an item correctly, the value would be 0.00. An item that everyone answers correctly would have a value of 1.00.
Desired score for classroom tests
A classroom test ideally is comprised of items with a range of difficulties that average around .5 (generally, item difficulties between .3 and .7).
Score band interpretation
P value | Difficulty | Description |
|---|---|---|
P > .70 | Easy | The correct answer is chosen by more than 70 percent of the students |
.30 < P < .70 | Average | The correct answer is chosen by 30-70 percent of the students |
P < .30 | Challenging | The correct answer is chosen by less than 30 percent of the students |
Corrective actions
Items that are too easy (p > .80) or too difficult (p < .30) do not contribute to test reliability and should be used sparingly. It's best to review additional indicators, such as item discrimination and point biserial to determine what action may be needed for these items.
Formula
This value is determined simply by calculating the proportion of students that answer the item correctly using the following formula: P = Np / N
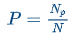
Np = number of students who answered correctly
N = number of students who answered
The correlation items include both dichotomous and non-dichotomous items (see the table to see which items are dichotomous or non-dichotomous). If an item is non-dichotomous, then the points earned may be partial points.
Dichotomous | Non-dichotomous |
|---|---|
|
|
Discrimination Index (D)
Item discrimination is a correlation value (similar to point biserial) that relates the item performance of students who have mastered the material to the students who have not. It serves as an indicator of how well the question can tell the difference between high and low performers.
Also Called: Item Discrimination
Score Range: -1.00 to 1.00
Items with higher values are more discriminating. Items with lower values are typically too easy or too hard. This matrix provides a simplified view of how items are determined to have high or low values.
Student Performs Well on Test | Student Performs Poorly on Test | |
|---|---|---|
Student Gets Item Right | High D | Low D |
Student Gets Item Wrong | Low D | High D |
Desired score for classroom tests
.20 or higher
Score band interpretation and color coding
Discrimination index | Interpreted score | Description |
|---|---|---|
D > .70 | Excellent | Best for determining top performers from bottom performers |
.60 < D < .70 | Good | Item discriminates well in favor of top performers |
.40 < D < .60 | Acceptable | Item discriminates reasonably well |
.20 < D < .40 | Needs Review | May need corrective action unless it is a mastery-level question |
D < .20 | Unacceptable | Needs corrective action |
Corrective actions
Items with low discrimination should be reviewed to determine if they are ambiguously worded or if the instruction in the classroom needs work. Items with negative values should be scrutinized for errors or discarded. For example, a negative value may indicate that the item was miskeyed, ambiguous, or misleading.
Formula
When calculating item discrimination, first all students taking the test are ranked according to the total score, then the top 27 percent (high performers) and the bottom 27 percent (low performers) are determined. Finally, item difficulty is calculated for each group and subtracted using the following formula: D= PH - PL
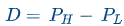
PH = item difficulty score for high performers
PL = item difficulty score for low performers
Point Biserial Correlation (rpb)
Point biserial is a correlation value (similar to item discrimination) that relates student item performance to overall test performance. It serves as an indicator of how well the question can tell the difference between high and low performers. The main difference between point biserial and item discrimination I is that every person taking the test is used to compute point biserial scores, and only 54% (27% upper + 27% lower) are used to compute the item discrimination scores.
Also Called: Item Discrimination II, Discrimination Coefficient
Score Range: -1.00 to 1.00
A high point biserial value means that students selecting the correct response are associated with higher total scores, and students selecting incorrect responses to an item are associated with lower total scores. Very low or negative point biserial values can help identify flawed items.
Desired score for classroom tests
.20 or higher
Score band interpretation
Biserial value | Interpreted score | Description |
|---|---|---|
rpb > .30 | Excellent | Best for determining top performers from bottom performers |
.20 < rpb < .30 | Good | Reasonably good, but subject to improvement |
.10 < rpb < .20 | Acceptable | Usually needs improvement |
rpb < .10 | Poor | Needs corrective action |
Corrective actions
Items with low discrimination should be reviewed to determine if they are ambiguously worded or if the classroom instruction needs work. Items with negative values should be scrutinized for errors or discarded. For example, a negative value may indicate that the item was miskeyed, ambiguous, or misleading.
Formula
Point biserial identifies items that correctly discriminate between high and low groups, as defined by the test as a whole, using the following formula: rpb = (Mp - Mq / St) √pq
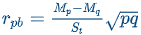
Mp = mean score for students answering the item correctly
Mq = mean score for students answering the item incorrectly
St = standard deviation for the whole test
p = proportion of students answering correctly
q = proportion of students answering incorrectly
Test statistics
Test statistics assess the performance of the test as a whole.
Cronbach's Alpha Reliability (Ɑ)
Cronbach's alpha is the test's consistency reliability based on the composite scores of its items. It serves as an indicator of the extent to which the test is likely to produce consistent scores.
Also called: Internal Consistency Reliability, Coefficient Alpha
Score Range: 0.00 to 1.00
High reliability means that students who answered a given question correctly were more likely to answer other questions correctly. Low reliability means that the questions tended to be unrelated in terms of who answered them correctly.
Desired score for classroom tests
.70 or higher
Score band interpretation and color coding
Alpha reliability | Interpreted score | Description |
|---|---|---|
P > .90 | Excellent | In the range of the best standardized tests |
.70 < Ɑ < .90 | Good | In the desired range of most classroom tests |
.60 < Ɑ < .70 | Acceptable | Some items could be improved |
.50 < Ɑ < .60 | Poor | Suggests the need for corrective action unless it purposely contains very few items |
Ɑ < .50 | Unacceptable | Should not contribute heavily to the course grade and needs corrective action |
Corrective actions
There are a few ways to improve test reliability.
Increase the number of items on the test.
Use items with higher item discrimination values.
Include items that measure higher, more complex levels of learning, and include items with a range of difficulty, with most questions in the middle range.
If one or more essay questions are included on the test, grade them as objectively as possible.
Formula
The standardized Cronbach's Alpha formula divides the reliability of items by the total variance in the composite scores of those items (a ratio of true score variance to total variance) using the following formula: α = kr / (1 + (k-1)r)
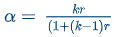
k = total number of items on the test
r = mean inter-item correlation
